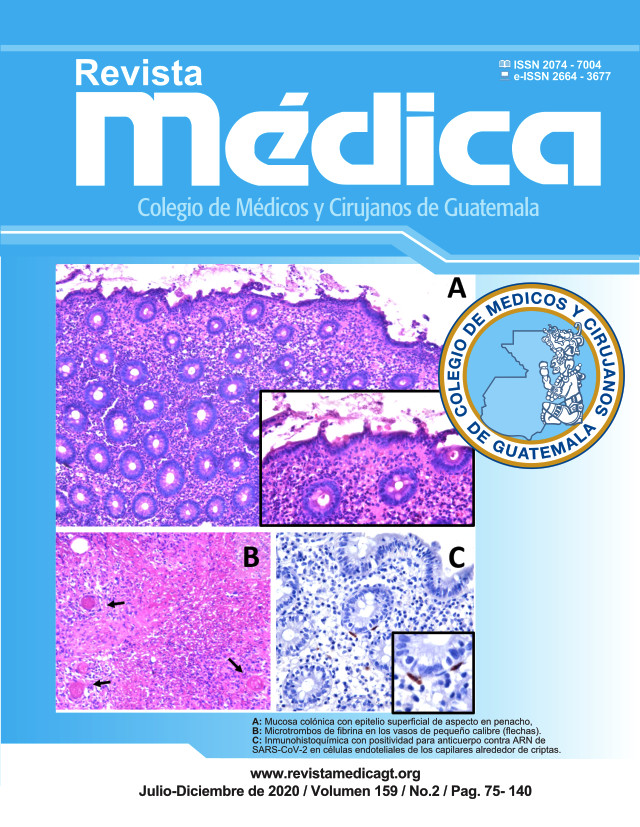
Mortality associated to COVID-19 in adult patients with chronic kidney disease in Guatemala
Article Details
Authors
Publication Information
Keywords
COVID19
Mortality
Guatemala
Abstract
Objective: to determine the prevalence of mortality associated to COVID-19 in patients with chronic kidney disease. Material and methods: descriptive and prospective study, carried out on 151 adult patients with chronic kidney disease who present COVID-19 infection and assisted to the permanent attention center of respiratory diseases in Hospital General San Juan de Dios, demographic characteristics, comorbidities, renal replacement therapy, kidney function tests and potassium, time of chronic kidney disease diagnosis and ventilatory support were determined, a data collection instrument was elaborated with all the variables of the study. Results: 57 (37.7%) of the total population of patients died, 66.7% were male, 35.1% had ages between 46-55 years, 78.9% had diabetes mellitus, 89.5% were undergoing hemodialysis therapy, 19.3% of patients were under invasive ventilatory support, 26 of these patients (45.6%) had more tan 11 days without dialytic therapy, according to laboratory findings 47.4% had creatinine levels between 9.1 and 12 mg/dL, 38.6% had blood urea nitrogen levels amid 90.1 and 110 mg/dL and potassium levels between 5.51 and 6.5 mmol/L. Conclusions: mortality associated to COVID-19 in chronic kidney disease patients was of 37.7%, this group of patients present an extended time amid each dialytic therapy and a higher mortality risk.
Graph - Number of readers per month
Downloads
How to Cite
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
 |
This work is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-SA 4.0) |
| Copyright notice |
| Authors will retain their copyright and assign to the journal the right of first publication of their work, which will be simultaneously subject to a Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International license (CC BY-NC-SA 4.0) that allows third parties to share the work as long as its author and its first publication in this magazine are indicated. | |
| Authors may adopt other non-exclusive license agreements for the distribution of the version of the published work (eg: deposit it in an institutional repository or publish it in a monographic volume) provided that the initial publication in this journal is indicated. | |
| Authors are allowed and recommended to disseminate their work through the internet (eg, in institutional telematic files or on their website) before and during the submission process, which can lead to interesting exchanges and increase citations of the published work. (See The effect of open access). |
| About the Creative Commons license |
|
|
You are free to: |
| Share — copy and redistribute the material in any medium or format. | |
| Adapt — remix, transform, and build upon the material. | |
| The licensor cannot revoke these freedoms as long as you follow the license terms. |
Under the following terms: |
| Attribution — You must give appropriate credit, provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made. You may do so in any reasonable manner, but not in any way that suggests the licensor endorses you or your use. | |
| NonCommercial — You may not use the material for commercial purposes. | |
| ShareAlike — If you remix, transform, or build upon the material, you must distribute your contributions under the same license as the original. |
|
| No additional restrictions — You may not apply legal terms or technological measures that legally restrict others from doing anything the license permits. |